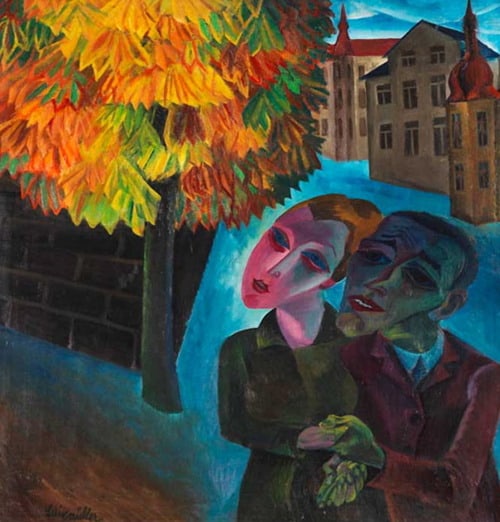
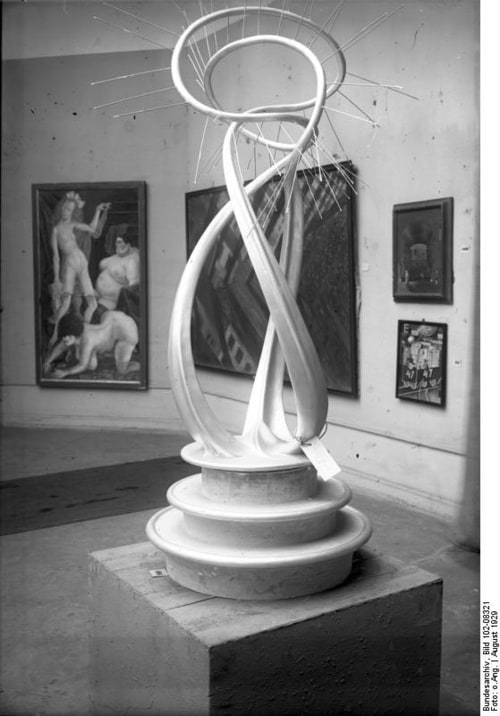
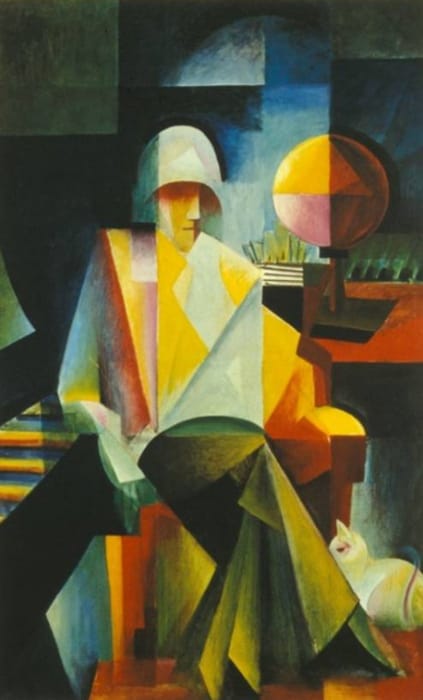
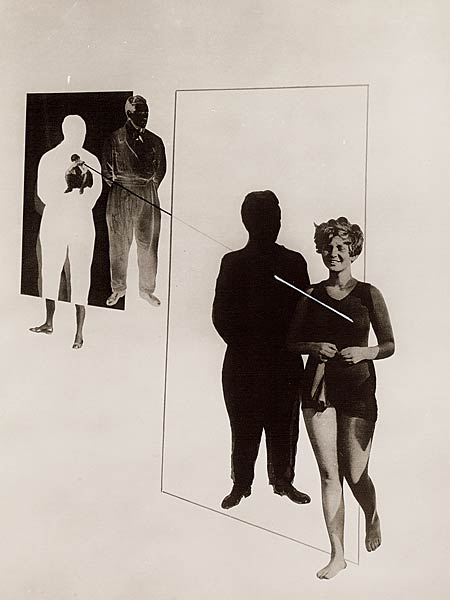
❝ Degenerate art: Artists in the 1937 Munich show
Sort by:
Showing 1-50 of 61
Rating:
List Type:

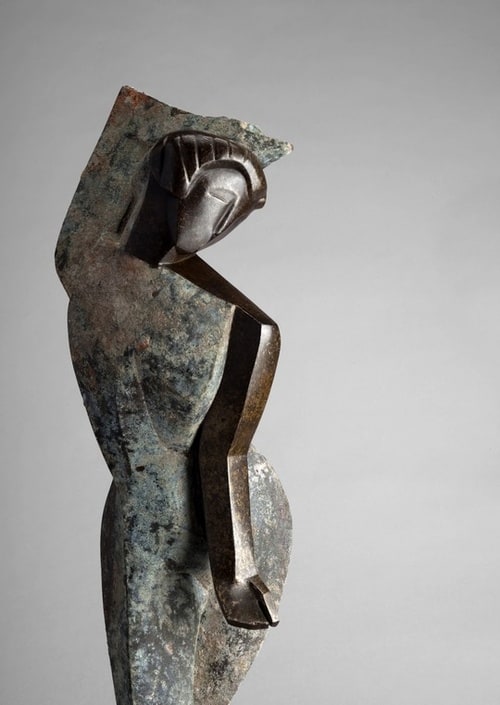
After 1925, Freundlich lived and worked mainly in France. In Germany, his work was condemned by the Nazis as degenerate and removed from public display. Some works were seized and displayed at the infamous Nazi exhibition of degenerate art including his monumental sculpture Der Neue Mensch (The New Man) which was photographed unsympathetically and used as the cover illustration of the exhibition catalogue. Der Neue Mensch was never recovered and is assumed to have been destroyed. One of his sculptures was recovered in an excavation in Berlin and put on display at the Neues Museum.


His varied color palettes, some with bright colors and others sober, perhaps reflected his alternating moods of optimism and pessimism.Germany in 1937, seventeen of Klee’s pictures were included in an exhibition of "Degenerate art" and 102 of his works in public collections were seized by the Nazis.
Nusch 's rating:



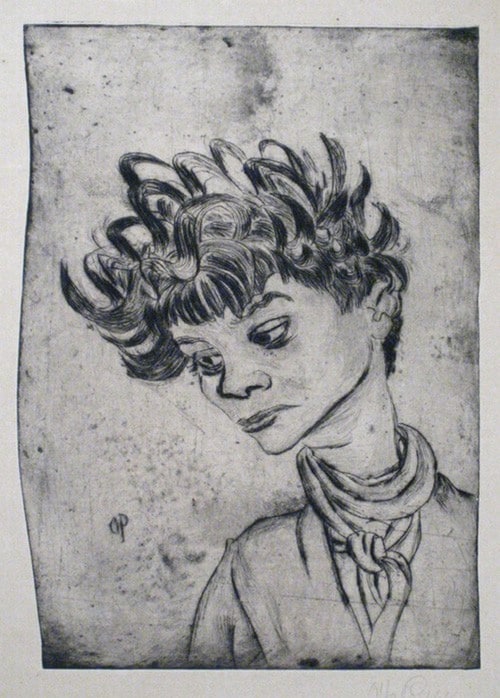
Elfriede Lohse Wächtler was a German painter of the avant-garde whose works were banned as "degenerate art", and in some cases destroyed, by the Third Reich. She was killed in a former psychiatric institution at Sonnenstein castle in Pirna under Action T4, a forced euthanasia program of Nazi Germany. Since 2000 a memorial center for the T4 program in the house commemorates her life and work in a permanent exhibition.
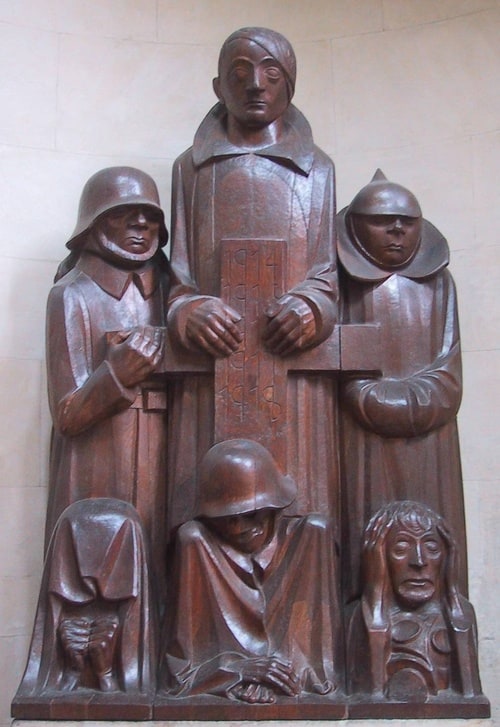

Das Magdeburger Ehrenmal (the Magdeburg cenotaph), by Ernst Barlach was declared to be degenerate art due to the "deformity" and emaciation of the figures—corresponding to Nordau's theorized connection between "mental and physical degeneration."

In 1933, Kirchner was labelled a "degenerate artist" by the Nazis and asked for his resignation from the Berlin Academy of Arts; in 1937, over 600 of his works were confiscated from public museums in Germany and were sold or destroyed. In 1938, the psychological trauma of these events, along with the Nazi occupation of Austria, close to his home, led to his suicide.
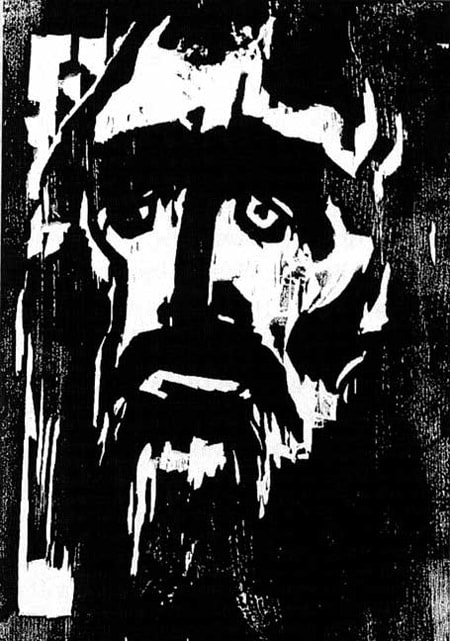

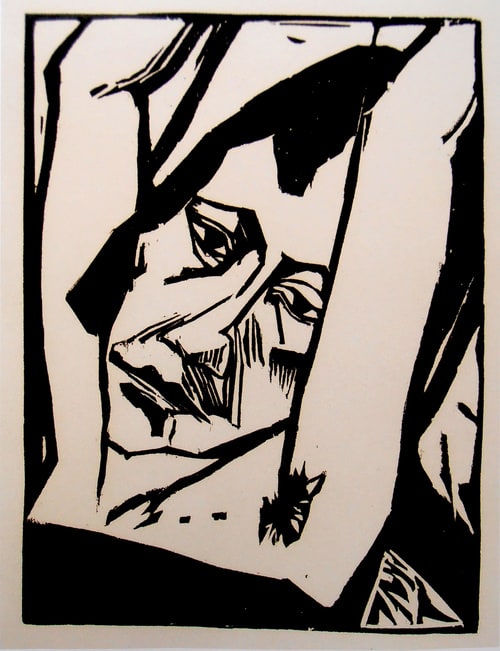
Membership in the Nazi Party did not protect Emil Nolde, whose 1912 woodcut The Prophet is shown here, from being proscribed by Hitler. 1,052 of Nolde's paintings were removed from German museums, more than any other artist.

Nazi raid on the Bauhaus in the 1930s resulted in the confiscation of Kandinsky's first three Compositions. They were displayed in the State-sponsored exhibit "Degenerate Art", and then destroyed (along with works by Paul Klee, Franz Marc and other modern artists).
Nusch 's rating:



In the years after World War I Klein was associated with Walter Gropius, though he turned down Gropius's offer of a teaching position at the Bauhaus. Through the 1920s and after, Klein devoted much of his work to designs for theater and film production. He was the set designer for Robert Wiene's 1920 film Genuine, and for the 1924 production of Ernst Toller's Hinkemann.
Klein was included in the famous Degenerate Art exhibition mounted by the Nazi regime in 1937. He was able to resume his career in theatrical design after World War II. He died in 1954, at Pansdorf near Lübeck.
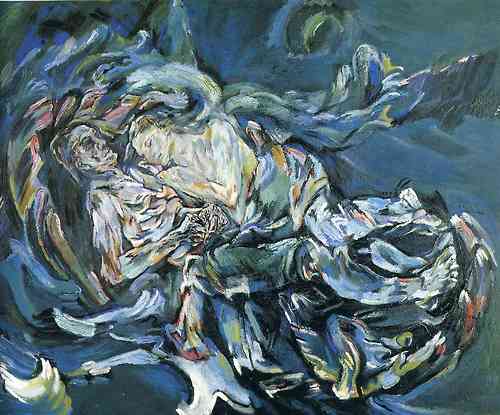

Deemed a degenerate by the Nazis, Kokoschka fled Austria in 1934 for Prague. In Prague his name was adopted by a group of other expatriate artists, the Oskar-Kokoschka-Bund (OKB), though he declined to otherwise participate. In 1938, when the Czechs began to mobilize for the expected invasion of the Wehrmacht, he fled to the United Kingdom and remained there during the war. With the help of the British Committee for Refugees from Czechoslovakia (later the Czech Refugee Trust Fund), all members of the OKB were able to escape through Poland and Sweden.
Nusch 's rating:



In 1937, twenty-five of his works were seized from public collections by the Nazis and four were shown in the Entartete Kunst (Degenerate Art) exhibition in Munich.

In 1938, upon his return from an exhibition of his work in Paris, Bauer was arrested by the Nazis for his "degenerate" art and for speculating on the black market — meaning selling his work to Guggenheim. The previous year Bauer’s work had been included in the infamous Degenerate Art show in Munich, organized by the Nazis to show all the deviant, abstract art. In spite of this Bauer had refused to move from his home country. Upon his arrest Bauer was held in a Gestapo prison for several months, as Rebay and Guggenheim worked to free him. After several false starts, he was finally released unconditionally in August 1938. During his time in prison, he created dozens of non-objective drawings on scavenged scraps of paper.

Marc gave an emotional meaning or purpose to the colors he used in his work: blue was used for masculinity and spirituality, yellow represented feminine joy, and red encased the sound of violence. After the National Socialists took power, they suppressed modern art; in 1936 and 1937, the Nazis condemned Marc as an entarteter Künstler (degenerate artist), and ordered that approximately 130 of his works be taken from exhibit in German museums.
Nusch 's rating:



On the 31st of March 1933, following the National Socialist rise to power, Baumeister was dismissed from his professorship at the Städel. Thereafter he earned his living mainly from commercial art, he was still however able to travel to Switzerland, Italy, and France. In the same year, his daughter Felicitas was born. In 1936 he was introduced by the Wuppertaler architect Heinz Rasch, with whom he work during the 1924 Exhibition in Stuttgart, to Dr. Kurt Herberts, the owner of a varnish factory in Wuppertal. He began working for the company in 1937, joining other artists ostracized by the National Socialist regime: Franz Krause, Alfred Lörcher, Georg Muche, and Oskar Schlemmer, and the art historian Hans Hildebrandt. That year five of his works were shown in the National Socialist exhibition Entartete Kunst (Degenerate art) in Munich.
Until 1941, when a ban on his paintings and exhibitions was issued by the National Arts Chamber, Baumeister still had many opportunities to exhibit his works abroad in Europe. Despite the prohibition and the constant surveillance, he still worked at the Herberts varnish factory, as well as on his art. In 1943, when a bomb attack rendered Wuppertal as well as Baumeister’s house in Stuttgart uninhabitable, he moved with his family to Urach in the Swabian Alps.
In 1928, Bayer left the Bauhaus to become art director of Vogue magazine's Berlin office. He remained in Germany far later than most other progressives. In 1936 he designed a brochure for the Deutschland Ausstellung, an exhibition for tourists in Berlin during the 1936 Olympic Games - the brochure celebrated life in the Third Reich, and the authority of Hitler. However, in 1937, works of Bayer's were included in the Nazi propaganda exhibition "Degenerate Art", upon which he left Germany.
Nusch 's rating:
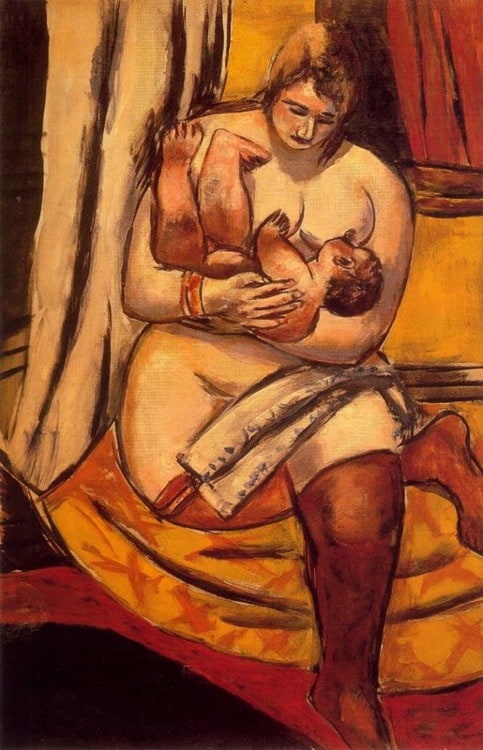



His fortunes changed with the rise to power of Adolf Hitler, whose dislike of Modern Art quickly led to its suppression by the state. In 1933, the Nazi government called Beckmann a "cultural Bolshevik" and dismissed him from his teaching position at the Art School in Frankfurt. In 1937 more than 500 of his works were confiscated from German museums, and several of these works were put on display in the notorious Degenerate Art exhibition in Munich. The day after Hitler's infamous radio speech about degenerate art in 1937, Beckmann left Germany with his second wife, Quappi. For ten years, Beckmann lived in poverty in self-imposed exile in Amsterdam, failing in his desperate attempts to obtain a visa for the US. In 1944 the Germans attempted to draft him into the army, despite the fact that the sixty-year-old artist had suffered a heart attack. =

When the Nazi regime came to power in 1933, he was among the many modernists condemned as degenerate artists, and prohibited from exhibiting. He moved to the Netherlands, where he spent the rest of his life working at the Rijksakademie in Amsterdam, first teaching Decorative Art, printmaking and stained-glass, then as the Academy Director.
Nusch 's rating:



Beginning during 1937 about twenty thousand works from German museums were confiscated as "degenerate" by a committee directed by Joseph Goebbels. Although the German press had once "swooned over him", the new German authorities now made a mockery of Chagall's art, describing them as "green, purple, and red Jews shooting out of the earth, fiddling on violins, flying through the air ... representing assault on Western civilization".
Nusch 's rating:
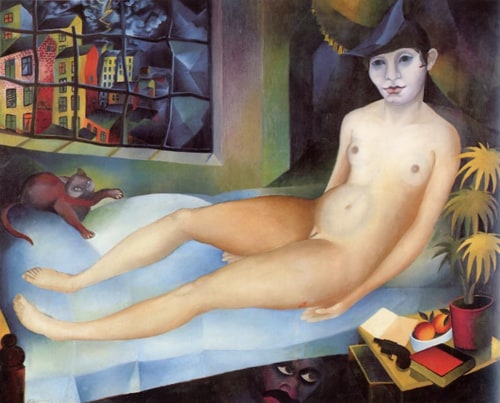



Davringhausen went into exile with the fall of the Weimar republic in 1933, first going to Majorca, then to France. In Germany approximately 200 of his works were removed from public museums by the Nazis on the grounds that they were degenerate art. Prohibited from exhibiting, Davringhausen was interned in Cagnes-sur-Mer but fled to Côte D' Azur. In 1945 however he returned to Cagnes-sur-Mer, a suburb of Nice, where he remained for the rest of his life. He worked as an abstract painter under the name Henri Davring until his death in 1970.
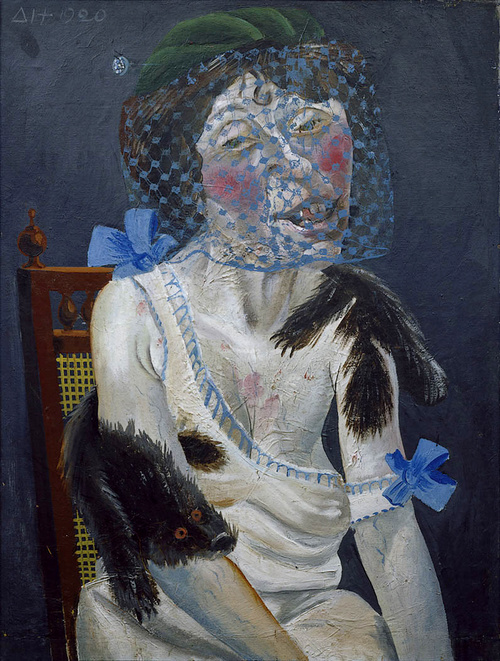

When the Nazis came to power in Germany, they regarded Dix as a degenerate artist and had him sacked from his post as an art teacher at the Dresden Academy. He later moved to Lake Constance in the southwest of Germany. Dix's paintings The Trench and War cripples were exhibited in the state-sponsored Munich 1937 exhibition of degenerate art, Entartete Kunst. They were later burned.
Dix, like all other practicing artists, was forced to join the Nazi government's Reich Chamber of Fine Arts (Reichskammer der bildenden Kuenste), a subdivision of Goebbels' Cultural Ministry (Reichskulturkammer). Membership was mandatory for all artists in the Reich. Dix had to promise to paint only inoffensive landscapes. He still painted an occasional allegorical painting that criticized Nazi ideals.
In 1939 he was arrested on a trumped-up charge of being involved in a plot against Hitler (see Georg Elser), but was later released.
Nusch 's rating:



“L’Ange du Foyer” (1937)
During the Nazi regime, works by Max Ernst were included in the 1937 “Entartete Kunst” (Degenerate Art) mockery exhibition, as examples of degradation in art.
Nusch 's rating:



Feibusch was born to Jewish parents and studied in Paris under Andre L'Hote. He was becoming successful as an artist when the Third Reich made his life in Germany impossible. He was one of the artists exhibited in the 1937 Degenerate Art Exhibition (Entartete Kunst) put on by the Nazis to highlight the modernist trends in art they opposed. Feibusch was one of a minority of artists included whose work was relatively conservative, and he was probably included for his Jewish heritage. His works in that exhibition, now lost, were two paintings of angels.

When the Nazi Party came to power in 1933, the situation became unbearable for Feininger and his wife. The Nazi Party declared his work to be "degenerate." They moved to America after his work was exhibited in the 'degenerate art' (Entartete Kunst) in 1936, but before the 1937 exhibition in Munich. He taught at Mills College before returning to New York.

He took part in the Hannoversche Sezession from 1918, where he met Kurt Schwitters, among others, and became friends with Theodor Däubler. His exhibition was banned, and he was named a degenerate artist in 1938.

Following the fall of the Weimar Republic, Grundig was declared a degenerate artist by the Nazis, who included his works in the defamatory Degenerate Art exhibition in Munich in 1937. He expressed his antagonism toward the regime in paintings such as The Thousand Year Reich (1936). Forbidden to practice his profession, he was arrested twice—briefly in 1936, and again in 1938, after which he was interned in Sachsenhausen concentration camp from 1940–1944.

Organised by Hausmann, Grosz and Heartfield, along with Max Ernst, the fair was to become the most famous of all Berlin Dada's exploits, featuring almost 200 works by artists including Francis Picabia, Hans Arp, Ernst, Otto Dix & Rudolf Schlichter, as well as key works by Grosz, Höch and Hausmann. The work Tatlin At Home, 1920, can be clearly seen in one of the publicity photos taken by a professional photographer; the exhibition, whilst financially unsuccessful, gained prominent exposure in Amsterdam, Milan, Rome and Boston.[13] The exhibition also proved to be one of the main influences on the content and layout of Entartete Kunst, the show of degenerate art put on by the Nazis in 1937, with key slogans such as 'Nehmen Sie DADA Ernst' (Take Dada seriously!) appearing in both exhibitions.

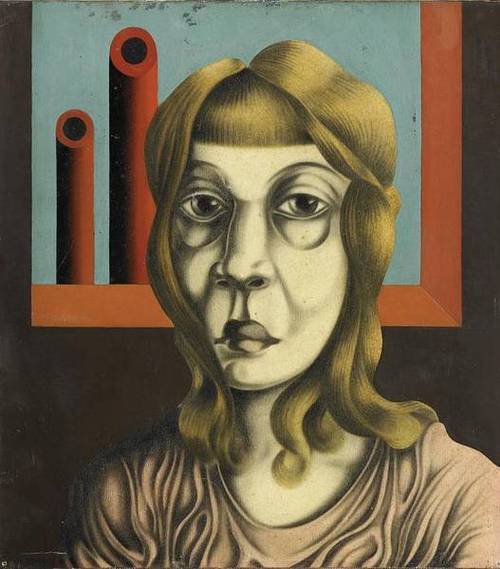
In 1937, The Nazis deemed his art “Degenerate.” 729 works were expelled from German museums. In January 1944, his studio was bombed and all of his blocks and plates were destroyed. He later moved to Lake Constance where he took up graphics again but these later works are overshadowed by the genius of his early works.

In 1929 he began publication of "a-z", a journal of progressive artists. He was among the many German artists whose works were condemned as degenerate art when the Nazis took power in 1933. He died in Cologne in 1936.
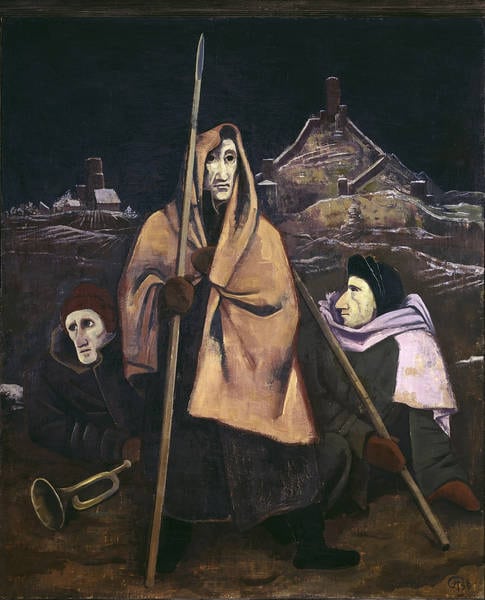

One of the most prominent painters of expressionism, he never was a member of one of the expressionist painting groups, like "Die Brücke", who influenced him. His work was considered degenerate art by the Nazis, and only after World War II did he regain recognition as one of the greatest German painters.
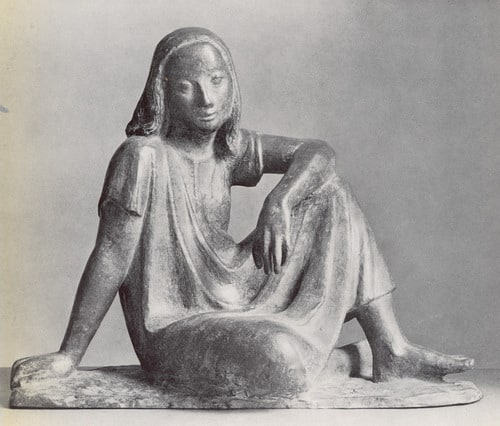

In September 1925, the Bauhaus was relocated to Dessau, and its Pottery Workshop was discontinued. Marcks moved instead to the Kunstgewerbeschule (School of Applied Arts) in Burg Giebichenstein near Halle. After the death of its director, Paul Thiersch, Marcks was named his replacement, a position he continued in until his dismissal in 1933. He was fired because his work was deemed unsuitable by the Nazis, with the result that several works were in the infamous exhibition of "degenerate art" in Munich in 1937, along with that of other Bauhaus artists, among them Herbert Bayer, Lyonel Feininger, Johannes Itten, Wassily Kandinsky, Paul Klee, Laszlo Moholy-Nagy, Oskar Schlemmer and Lothar Schreyer.
Despite such persecution, Marcks continued to live in Germany (in Mecklenburg) throughout World War II. In 1937, when twenty-four of his works were confiscated and destroyed by the Nazis, he was prohibited from exhibiting and threatened with being forbidden to work. During this period, he made several trips to Italy, where he worked in the Villa Romana in Florence and the Villa Massimo in Rome. In 1943, his studio in Berlin was bombed during an air raid, and many of his works destroyed.
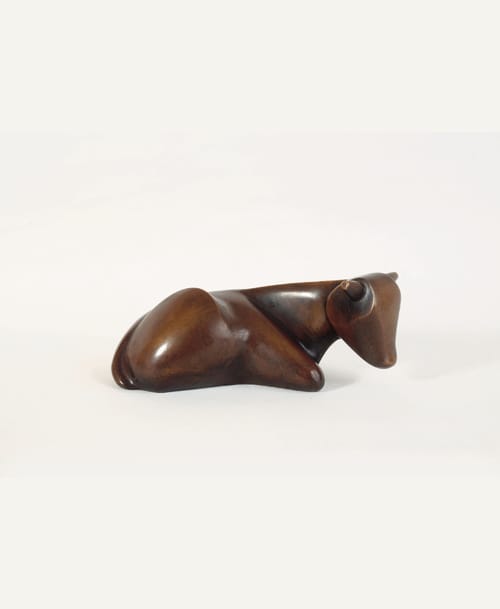

Mataré was denounced as "degenerate" and expelled from his position. One of his sculptures "Die Katze" (The cat) was placed into the exhibition of shame and derision "Entartete Kunst" (Degenerate Art) staged by the Nazis in Munich, 1937.
Nusch 's rating:
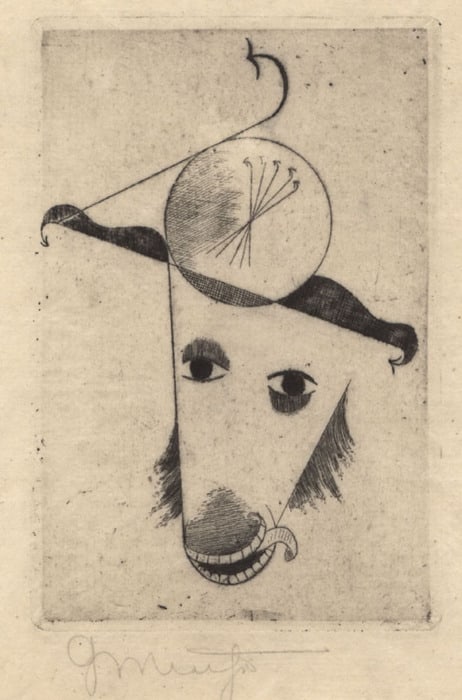



Thirteen Muche paintings and two prints were confiscated from museums by the Nazis and at least two of those works were displayed in the 1937 Munich exhibition Entartete Kunst (Degenerate Art).

In 1937 the Nazis seized 357 of his works from German museums, since the pictures were considered to be degenerate art.

Two of his works were shown in the notorious exhibition of "Degenerate art" and Nay was forbidden to exhibit any longer. He wasn't even allowed to paint nor buy ready made colours.
Load more items (11 more in this list)
Degenerate art is the English translation of the German entartete Kunst, a term adopted by the Nazi regime in Germany to describe virtually all modern art. Such art was banned on the grounds that it was un-German or Jewish Bolshevist in nature, and those identified as degenerate artists were subjected to sanctions. These included being dismissed from teaching positions, being forbidden to exhibit or to sell their art, and in some cases being forbidden to produce art entirely.
Degenerate Art was also the title of an exhibition, mounted by the Nazis in Munich in 1937, consisting of modernist artworks chaotically hung and accompanied by text labels deriding the art. Designed to inflame public opinion against modernism, the exhibition subsequently traveled to several other cities in Germany and Austria.
While modern styles of art were prohibited, the Nazis promoted paintings and sculptures that were traditional in manner and that exalted the "blood and soil" values of racial purity, militarism, and obedience. Similarly, music was expected to be tonal and free of any jazz influences; films and plays were censored.
Added to
People who voted for this also voted for
Mexico. Favorite movies.
Existentialism - some titles
Movies of 70s : Top 70 and Others
Two Women Movie
Surrealist painters and their precursors
Lists not to look at just before bed
My Favorite Underrated Films
British Cinema
Movie checklists
France. Favorite movies.
1890's films
World Cinema - Czech Republic
World Cinema - Brazil
My favorite finnish movies
Top 10 Buster Keaton Films: Shorts
More lists from Nusch
Clowns ♥
Favorite lists published in 2012
PHOTOS | Man Ray
Obscure Lists
music photographers
John Waters Favorite Films
Green & Orange
 Login
Login

 3.5
3.5
 0
0